Leave Your Message
Understanding electrical conductors and insulators is essential in various fields. These materials play a crucial role in our daily lives. Electrical conductors allow the flow of electricity. Insulators, on the other hand, resist electrical flow.
In this exploration, let's dive deeper into the characteristics of the top electrical conductor and insulator materials. Copper is a prime example of an excellent conductor. It is widely used in wiring due to its efficiency. Rubber serves as a common insulator, preventing unintended electrical contact. However, not all conductors work efficiently in every situation. Similarly, some materials labeled as insulators may allow minimal current flow under specific conditions.
As we examine these materials, it’s vital to reflect on their applications. The choice between a conductor and insulator impacts safety and functionality. By understanding these aspects, we learn to appreciate the importance of selecting the right material for each task. Let's embark on this journey into the world of electrical conductor insulator dynamics.
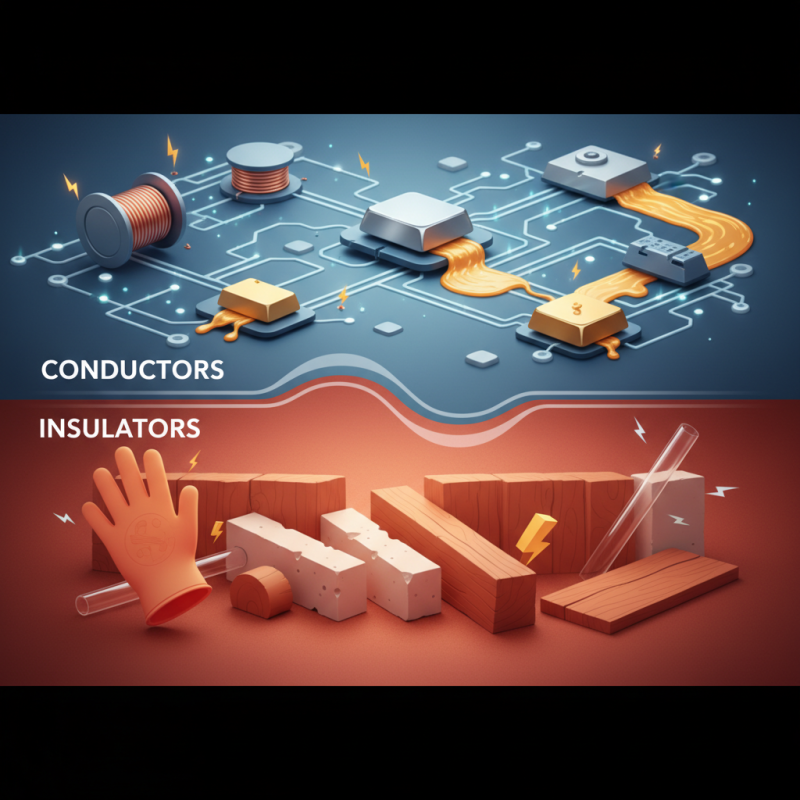
Electrical conductivity is a crucial concept in understanding how materials interact with electric currents. Conductors allow electrons to flow freely, while insulators impede this flow. Copper, for example, is often used in wiring due to its excellent conductivity. The arrangement of atoms in a material determines its conductive properties. In conductors, electrons can move easily, creating a reliable pathway for electricity.
On the other hand, insulators, like rubber and glass, have tightly bound electrons. This makes it difficult for electric currents to flow. The difference in electrical conductivity between materials is significant. It is interesting to note how some semiconductors can behave as both conductors and insulators under different conditions. For instance, silicon can conduct electricity if doped with impurities, highlighting the complexity of materials. Reflecting on these concepts reveals a layered understanding of how we utilize these materials in real-world applications.

When discussing electrical conductors, several materials stand out due to their exceptional properties. Copper is widely recognized for its excellent conductivity. Research shows it has a conductivity of about 59.6 x 10^6 S/m. Similarly, aluminum is also a popular choice, particularly in overhead power lines, due to its light weight and good conductivity. Its conductivity reaches approximately 36.9 x 10^6 S/m.
Gold and silver are other top conductors. Silver boasts the highest electrical conductivity at around 63 x 10^6 S/m. However, its cost limits widespread applications. On the other hand, gold's resistance to corrosion facilitates its use in high-end electronics and connectors.
**Tips:** Always consider the cost versus performance, especially if using precious metals. When choosing a conductor, think about the environment it will operate in. This can affect longevity and effectiveness.
Some materials like graphite and certain polymers also exhibit conductive properties. For example, graphite has a unique layered structure. It makes it suitable for specific applications despite lower conductivity (about 3 x 10^6 S/m). Each conductor has its place but reflects the balance between function and practicality.
**Tips:** Assess the specific requirements of your application before making material choices. Not every conductor suits every need.
Insulators are crucial in controlling electrical flow and ensuring safety. Materials like rubber, glass, and ceramics are highly effective insulators. Their primary role is to prevent unwanted current leakage. For instance, rubber has a high dielectric strength, making it ideal for protecting wires and cables. According to recent industry reports, rubber can withstand over 20,000 volts per millimeter.
Ceramics also shine in high-temperature applications. They are often used in insulators for power lines or high-voltage equipment. With the ability to withstand extreme conditions, ceramics are indispensable in utility infrastructures.
**Tip:** Consider the operating environment for insulators. Different materials perform better under specific conditions.
Another essential category includes plastics, such as PVC and polyethylene. These materials are lightweight and flexible. They are widely used in household electrical applications. However, some plastics degrade over time due to UV exposure. Regular checks can prevent hazards and ensure longevity.
**Tip:** Always check the insulation rating before purchasing materials. An inappropriate choice can lead to performance issues.
During installation, proper handling is critical. Insulation can easily be damaged if not treated correctly. Avoid using tools that can cut or scratch the surface. This can expose the conductor and compromise safety.
When comparing conductors and insulators, we dive into essential aspects of electricity. Conductors allow electric currents to flow with ease, while insulators resist this flow. Understanding these differences is crucial in both everyday applications and industrial settings.
For homeowners, knowing which materials conduct electricity helps avoid hazards. For instance, copper wires are excellent conductors, found in most electrical systems. In contrast, rubber gloves protect against electric shock due to their insulating properties. However, not all insulators are perfect. Some can wear down over time, leading to potential risks.
**Tip:** Regularly inspect your electrical cords. Look for signs of wear, such as fraying or cracks. This simple check can prevent accidents.
Another key aspect is energy efficiency. Using the right conductor can minimize electricity loss. It’s often overlooked how much energy can be wasted through poor connections. Not using insulation properly can increase energy costs.
**Tip:** When installing new appliances, consider using high-quality insulation materials. It might save you money in the long run. A little extra effort can lead to significant benefits.
Electrical conductors and insulators play vital roles in everyday technology. Conductors, like copper and aluminum, allow electricity to flow easily. This characteristic is crucial in power lines, which transport electricity over long distances. Insulators, such as rubber and glass, prevent unwanted electrical flow. They are essential in protecting us from electric shocks.
Consider power tools. They use conductors to operate effectively. However, without proper insulation, the user is at risk. Quality insulators keep the user safe while ensuring the tool performs well. Another example is household wiring. Good insulation prevents short circuits. Yet, the aging of materials can lead to dangerous situations. It’s a reminder of how important regular maintenance is.
In electronics, conductors and insulators are intertwined. Circuit boards rely on both to function properly. Often, we take this for granted until a failure occurs. Reflections on this can lead us to appreciate the balance of design and safety. Ideal conductors and insulators enhance technology, but imperfections always exist. Such challenges evoke constant innovation.