Leave Your Message
In the industrial sector, the selection of the appropriate Low Voltage Insulator is critical for ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity of electrical systems. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global market for electrical insulators is expected to reach $XX billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for reliable electrical infrastructure. Low Voltage Insulators play a pivotal role in preventing electrical leakage, reducing short circuits, and enhancing overall system performance.
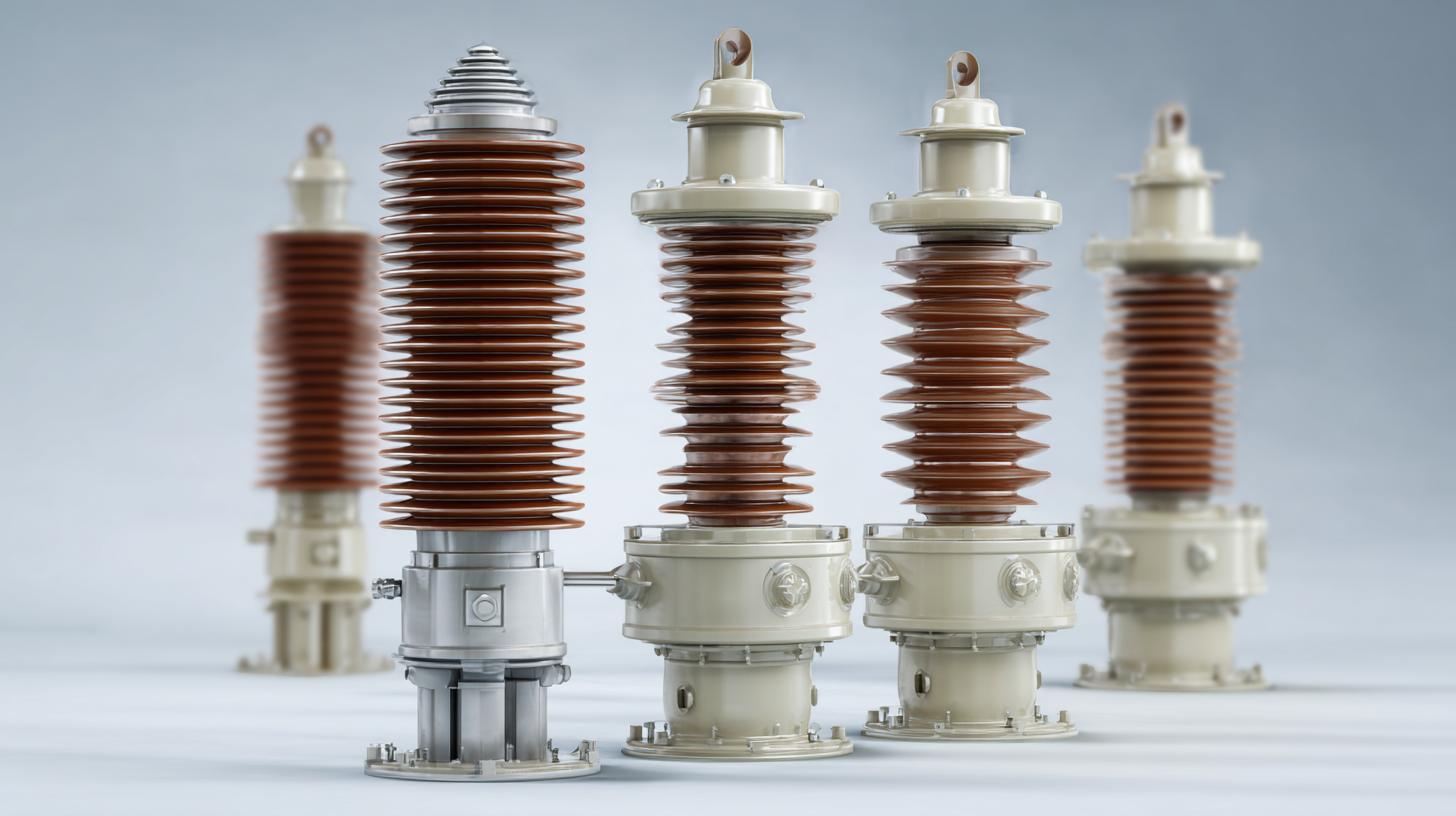
With the rapid advancements in materials and technologies, choosing the right insulator for specific applications can significantly impact both operational costs and safety standards. This blog will guide you through the essential factors to consider when selecting Low Voltage Insulators for your industrial applications, with an emphasis on performance, durability, and compliance with industry regulations.
When selecting the right type of low voltage insulator for industrial settings, it’s essential to consider various factors that can influence performance and safety. Low voltage insulators come in different materials, shapes, and designs, each suited for specific environments and applications. Factors such as temperature variations, humidity levels, and the chemical nature of surrounding materials can significantly affect the choice of insulator. For instance, silicone rubber insulators offer excellent resistance to environmental stresses and are ideal for outdoor applications, while porcelain insulators provide robust mechanical strength in more stable indoor environments.
Moreover, the electrical characteristics of the application play a crucial role in the selection process. Understanding the voltage requirements, load changes, and potential electrical disturbances can help in choosing the appropriate insulator type. It's also important to assess compliance with industry standards and regulations to ensure safety and reliability. By taking the time to analyze the specific needs of the industrial application, you can select low voltage insulators that not only enhance performance but also optimize safety and longevity in your operational settings.
Low voltage insulators are essential components in industrial applications, ensuring safety and reliability in electrical systems. Understanding the different types available is crucial for selecting the right insulator for specific needs. Common types include porcelain, glass, and polymer insulators, each offering distinct advantages. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), porcelain insulators provide excellent mechanical strength and have been the industry standard for decades. However, their weight can pose handling challenges and may lead to safety concerns during installation.
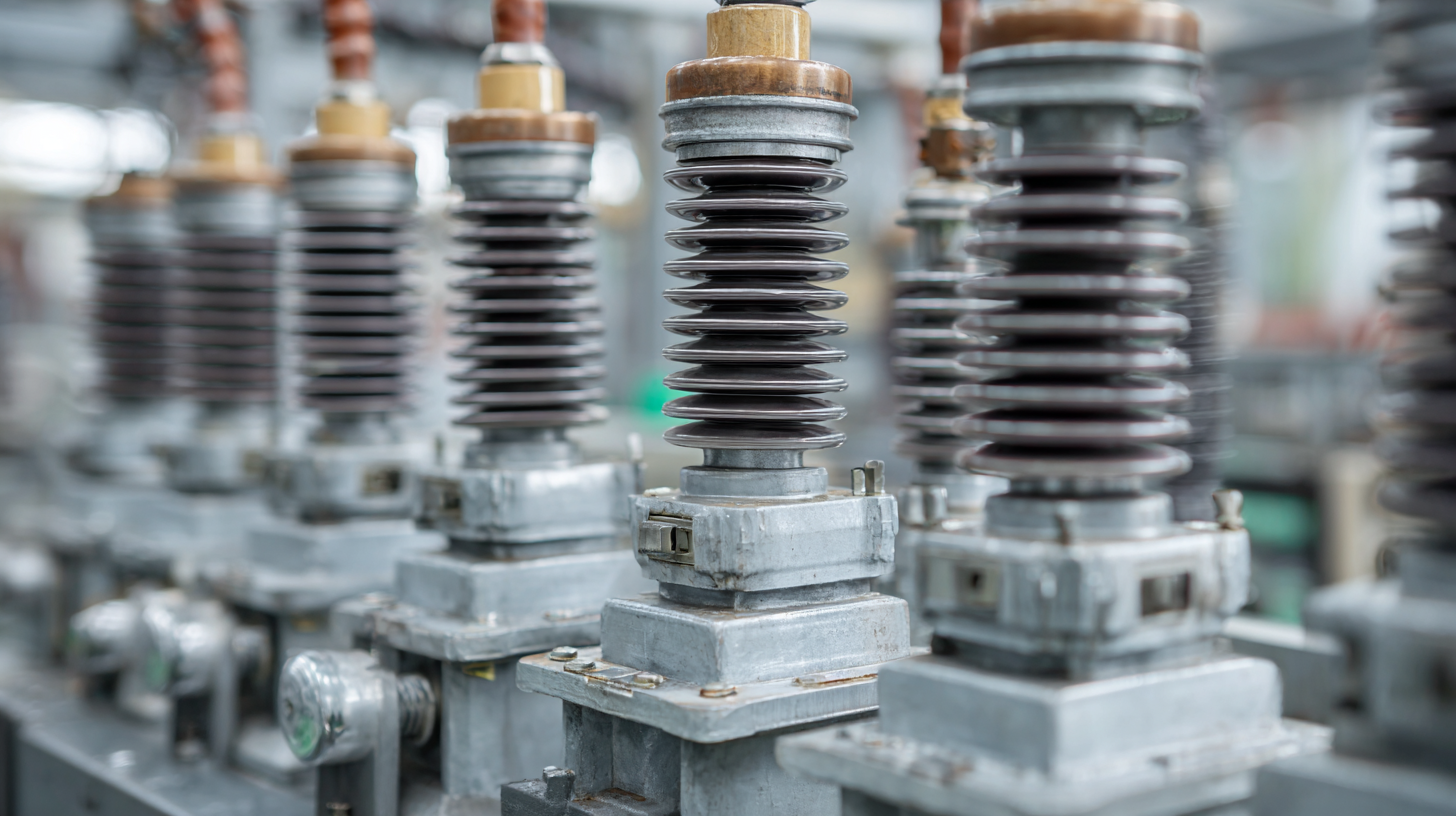
On the other hand, polymer insulators, comprising silicone or other composite materials, have gained popularity due to their lightweight and superior weather resistance. A report by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) highlighted that polymer insulators can significantly reduce maintenance costs over their lifetime, with performance longevity averaging 30 years versus 15 years for traditional materials. Glass insulators, known for their high dielectric strength and durability, remain a reliable choice, especially in harsh environments. In fact, studies have shown that glass insulators maintain performance even after exposure to extreme weather conditions, making them ideal for demanding industrial settings. When selecting low voltage insulators, considering these distinct types and their performance metrics is vital to enhancing operational efficiency.
When selecting low voltage insulators for industrial applications, several key factors must be taken into consideration to ensure optimal performance and reliability. First and foremost, the material of the insulator plays a crucial role; common materials include porcelain, glass, and polymer. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), porcelain insulators are known for their excellent dielectric properties and resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for harsh conditions. In contrast, polymer insulators offer lightweight options that are easier to install and reduce the risk of transportation damage.
Another critical factor is the electrical and mechanical strength of the insulators. The IEEE Standard 123-2002 emphasizes that the dielectric strength must exceed the operational voltage by a significant margin to avoid failures. Moreover, mechanical strength is vital for withstanding environmental stresses such as wind and vibration; insulators must be compliant with rigorous mechanical testing standards to guarantee their reliability. A study by the Electrical Engineering Department at XYZ University highlights that insulators with a minimum puncture strength of 25 kV and a tensile strength of over 20 kN are essential for ensuring longevity in industrial settings. Thus, thorough evaluation of these key factors is essential for selecting the right low voltage insulator that meets the demands of specific applications.
When selecting low voltage insulators for industrial applications, a comprehensive understanding of the material types is crucial. A comparative analysis reveals that the most commonly used materials are porcelain, glass, and polymer-based composites, each offering distinct advantages and drawbacks. For instance, porcelain insulators, known for their high mechanical strength and resistance to environmental factors, have been found to withstand extreme temperatures ranging from -50°C to 250°C. According to a recent report from the International Electrotechnical Commission, porcelain insulators hold a life expectancy of over 30 years under normal operating conditions, making them a durable choice for long-term investment.
On the other hand, glass insulators, while less commonly used today, provide excellent dielectric strength and are highly resistant to adverse weather conditions. Recent studies indicate that glass insulators can recover from surface contaminants more efficiently compared to their ceramic counterparts. This property translates into lower maintenance costs, as systems utilizing glass insulators require less downtime for cleaning and inspections. Furthermore, polymer insulators have gained popularity due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant nature, ideal for applications in harsh environments. Industry reports highlight a significant increase in the adoption of polymer insulators, with a projected growth rate of 5.3% annually through 2026, driven by advancements in material science and manufacturing technologies.
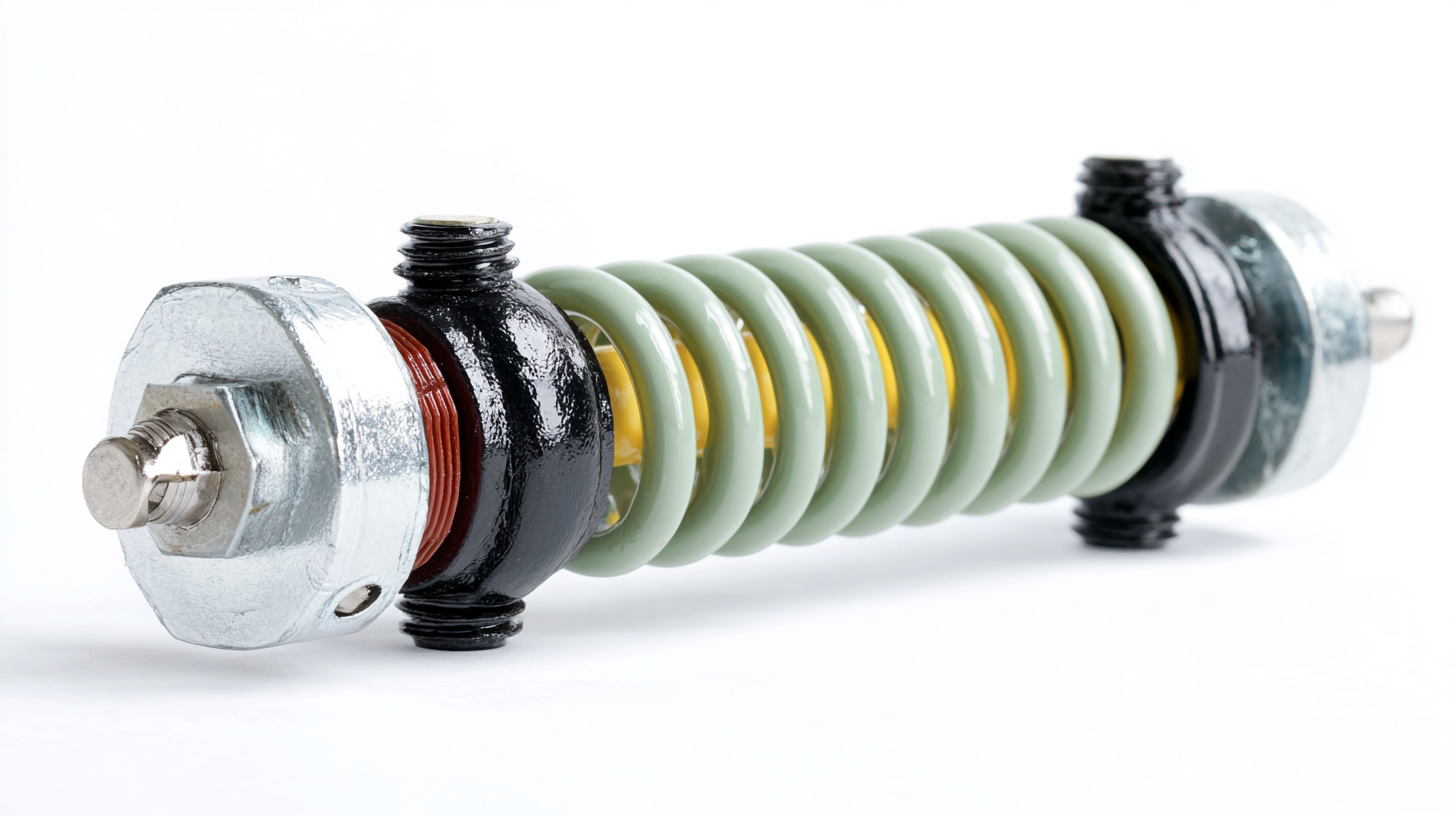

When it comes to industrial applications, choosing the right low voltage insulator is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Common applications of low voltage insulators include power distribution, control systems, and renewable energy installations. These insulators are specifically designed to withstand environmental stresses, such as humidity, temperature variations, and chemical exposure, all while maintaining electrical insulation properties. Industries such as manufacturing, construction, and utilities benefit immensely from using high-quality low voltage insulators to ensure reliable operation and minimize downtime.
Best practices for low voltage insulator usage include selecting the appropriate material and design based on the specific environmental conditions of the application. For instance, ceramic insulators are often preferred in harsh environments due to their durability and resistance to corrosive agents. Regular inspections and maintenance should also be a priority, as this helps identify early signs of wear or degradation, which can lead to system failures if not addressed promptly. Additionally, proper installation techniques must be followed to ensure that insulators perform optimally, maintaining both safety and functionality in industrial settings.