Leave Your Message
When it comes to electrical systems, selecting the right components is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. One such component that often goes overlooked is the low voltage insulator. Low voltage insulators play a vital role in preventing electrical leakage and ensuring reliable operation in various applications, from residential wiring to industrial setups. With a wide array of options available on the market, choosing the best low voltage insulator can seem daunting. However, understanding the key factors that influence your decision can simplify the process significantly. In this guide, we will explore seven essential factors to consider when selecting a low voltage insulator tailored to your specific needs, empowering you to make informed choices that enhance the safety and reliability of your electrical installations.
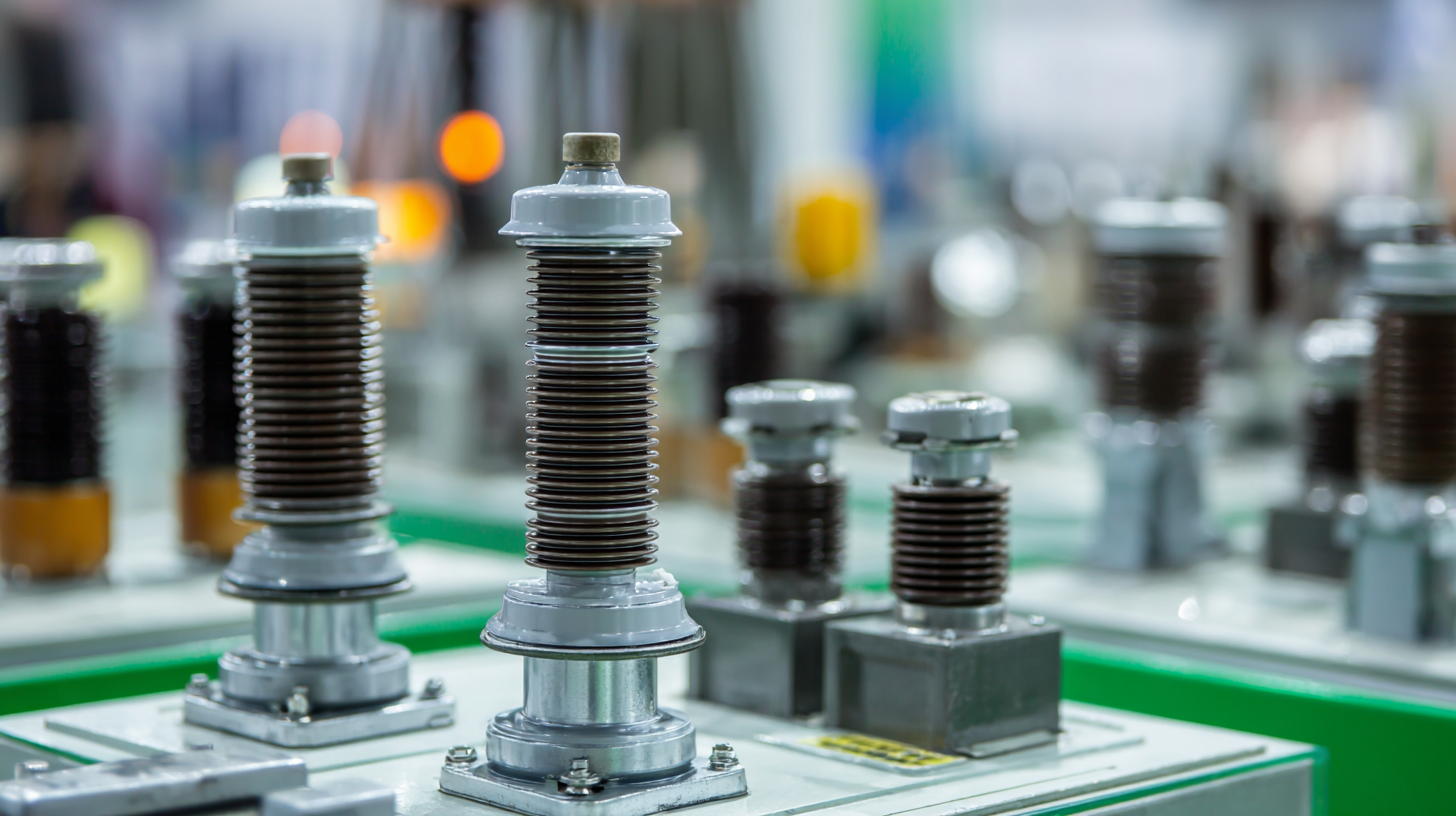
Low voltage insulators play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Fundamentally, these devices are designed to support and separate electrical conductors, preventing unwanted flow of electricity. Understanding the basic functions of low voltage insulators is essential for anyone involved in electrical installations or maintenance. Typically made from materials like porcelain, glass, or synthetic polymers, these insulators must withstand environmental stressors such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to moisture.
When selecting the right low voltage insulator, it's important to consider several factors beyond just material choice. The dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and installation environment greatly influence the performance of the insulator. For example, insulators intended for outdoor use may need to resist UV radiation and severe weather conditions. Additionally, knowing the voltage rating and electrical load requirements of your system can help you make an informed decision. By comprehensively understanding these aspects, you can ensure reliable insulation performance and minimize risks in your electrical network.
When selecting a low voltage insulator, understanding the key material considerations is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Insulators can be made from various materials, including porcelain, glass, and polymer composites, each offering distinct advantages. According to a recent industry report by Research and Markets, the global electrical insulator market is projected to reach $19.3 billion by 2026, with a significant uptick in demand for polymer insulators due to their lightweight nature and resistance to environmental stressors.
Polymer insulators, particularly those made from silicone rubber, are increasingly favored for low voltage applications due to their superior hydrophobic properties and long-term reliability. A study published by the IEEE indicates that silicone rubber insulators can provide more than 15 years of service life, even in aggressive environmental conditions, compared to traditional materials that may degrade much faster. This longevity translates to lower maintenance costs and reduced downtime, making them an economically advantageous choice for utility companies.
Furthermore, the thermal and electrical properties of the materials used in insulators significantly impact their efficiency. Materials with high dielectric strength, as noted in the Electrical Insulation Research Journal, can reduce energy losses and improve overall system reliability. Thus, choosing the right material not only optimizes performance but also aligns with sustainability goals by minimizing environmental impact through extended service life and reduced material waste.
When choosing the best low voltage insulator for your application, evaluating voltage ratings and electrical properties is paramount. According to the International Electro-technical Commission (IEC), insulators must adequately withstand the operating voltage without degrading over time. Typically, low voltage insulators are rated for voltages up to 1,000 volts. However, specific applications may necessitate insulators with higher performance ratings to ensure long-term reliability and safety.
Additionally, the electrical properties of insulators, such as dielectric strength and electrical conductivity, play a critical role in selection. A report by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) emphasizes that dielectric strength can vary significantly based on material composition. For example, porcelain insulators generally exhibit higher dielectric strength compared to polymer insulators, making them suitable for environments prone to insulation deterioration. Understanding these electrical properties allows engineers and procurement specialists to effectively assess insulator options tailored to their specific operational conditions, ultimately leading to improved system performance and safety.

When selecting low voltage insulators, environmental factors play a critical role in ensuring optimal performance and durability. For applications subjected to harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, or corrosive environments, it is essential to choose materials that can withstand these challenges. For instance,
silicone rubber insulators
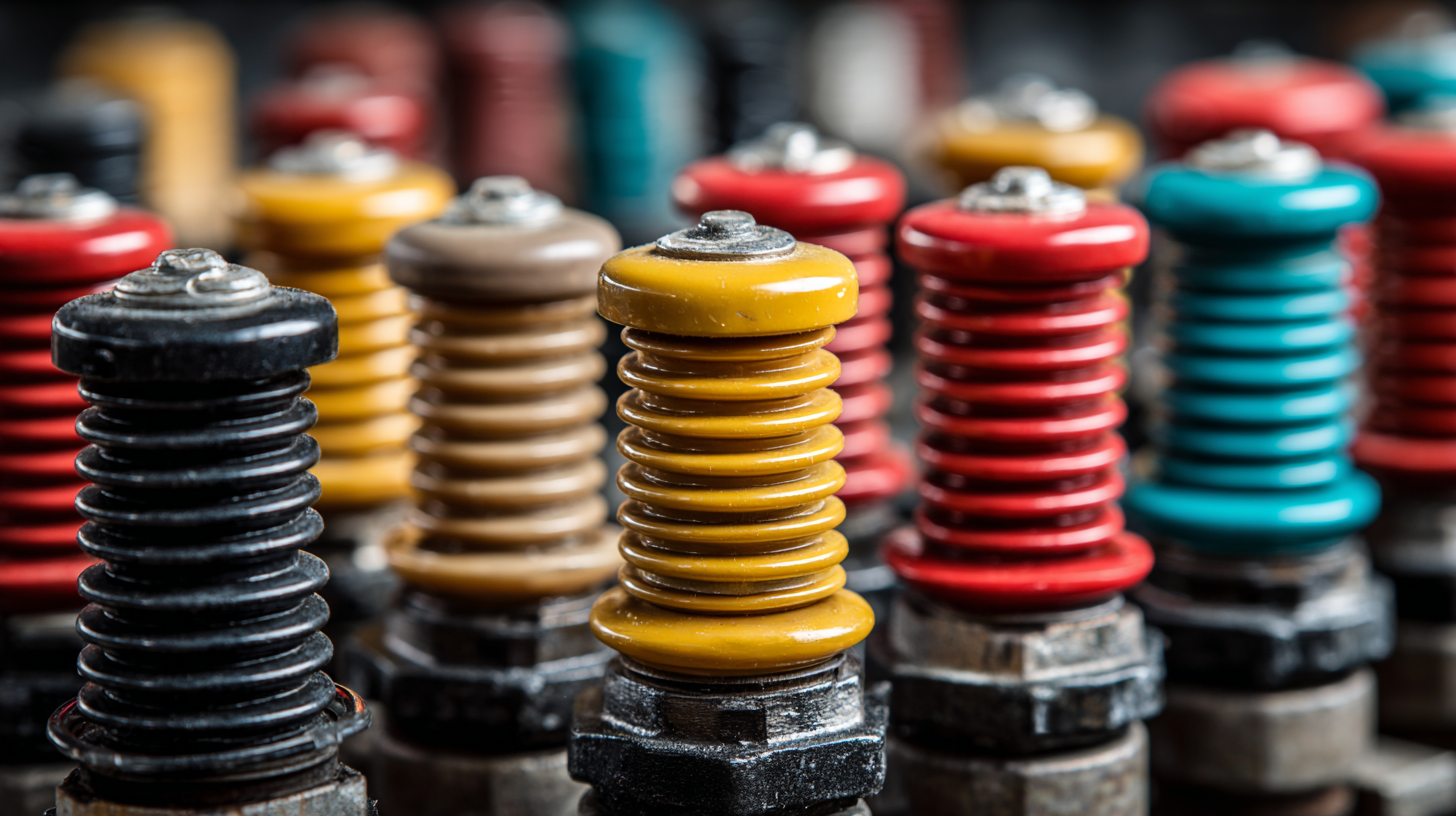 provide excellent resistance to UV radiation and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for outdoor installations that face direct sunlight or fluctuating weather patterns.
provide excellent resistance to UV radiation and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for outdoor installations that face direct sunlight or fluctuating weather patterns.
In addition to temperature and moisture, pollution is another environmental factor that must not be overlooked. Insulators installed in urban or industrial settings may be exposed to contaminants like dust, salt, and chemicals, which can compromise their integrity over time. Therefore, it is crucial to select insulators with a high level of pollution resistance, such as those treated with hydrophobic coatings or made from composite materials designed for such environments. By understanding the specific environmental challenges of your installation site, you can make a more informed decision and ensure the longevity and reliability of your low voltage insulators.
When it comes to low voltage insulators, proper installation is crucial for ensuring their longevity and efficiency. First, always ensure that the insulator is installed according to the manufacturer's guidelines. This includes using appropriate tools and techniques, such as securing connections firmly but without over-tightening, which can cause damage. Make sure the insulator is placed in a location where it can withstand environmental factors like wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations. Adequate spacing from nearby conductive materials is also essential to prevent any unintentional electrical contact.
Regular maintenance checks are vital to sustaining the performance of low voltage insulators. Inspect insulators regularly for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage, and clean them appropriately to remove dirt and debris that might impede their function. Seasonal checks can help catch issues early, allowing for timely repairs or replacements before they lead to more significant problems. Additionally, maintaining proper vegetation clearance around the installation site can reduce the risk of vegetation interference, which can compromise insulator performance. By adhering to these installation and maintenance tips, you can ensure that your low voltage insulators function efficiently and effectively for an extended period.
| Factor | Description | Recommended Material | Maintenance Frequency | Longevity Expectation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | Ensure the insulator can handle the applied voltage levels. | Ceramic or Composite | Annually | 10-30 years |
| Environmental Conditions | Consider exposure to chemicals, salt, and temperature extremes. | Polymeric Materials | Semi-Annually | 15-25 years |
| Mechanical Strength | Assess tensile and bending strength to avoid breakage. | Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer | Annually | 20-40 years |
| Electrical Properties | Check dielectric strength and insulation resistance. | Silicone Rubber | Twice a Year | 15-30 years |
| Installation Method | Follow proper guidelines to ensure stability and reliability. | Standard Mounting Accessories | N/A | N/A |
| Cost Effectiveness | Evaluate life-cycle costs versus initial expenses. | Low-Cost Insulating Materials | Annually | 10-20 years |
| Manufacturer Reputation | Research the track record and reviews of the manufacturer. | Reputable Industry Brands | N/A | N/A |
