Leave Your Message
Choosing the right Medium Voltage Insulator is crucial for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of electrical systems. With the global demand for electricity projected to grow by nearly 2.6% annually from 2021 to 2026, the role of reliable insulators has become increasingly significant. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), as more renewable energy sources are integrated into the power grid, the need for robust and high-performance insulators is essential to manage the challenges posed by fluctuating supply and demand.
Insulators serve as a vital link in maintaining the integrity of electrical systems by preventing leakage currents and ensuring high dielectric strength. A report from the Grand View Research states that the global insulated materials market is expected to reach $106.5 billion by 2024, indicating a strong emphasis on advanced materials that enhance performance and longevity for Medium Voltage Insulators. The selection process involves assessing various factors such as environmental conditions, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, which directly impact the insulator's performance over its lifecycle.
As we delve into the intricacies of selecting the appropriate Medium Voltage Insulator, it’s essential to understand the existing standards and performance metrics that guide this critical decision. Proper selection minimizes operational risks, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures compliance with industry regulations, ultimately leading to a more efficient and reliable electrical infrastructure.

Medium voltage insulators play a crucial role in the reliability and performance of electrical systems operating in the range of 1 kV to 35 kV. They serve to isolate electrical conductors from each other and from the ground, thereby preventing short circuits and ensuring the safety of both equipment and personnel. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), approximately 30% of power outages in urban areas can be attributed to insulator failure, underscoring the importance of selecting the right insulator for specific environmental conditions and operational demands.
When assessing medium voltage insulators, it is essential to consider factors such as material composition, environmental stress, and pollution levels. Materials commonly used include porcelain, glass, and polymer-based composites, each offering distinct advantages in terms of mechanical strength and resistance to electrical tracking and erosion. The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) notes that composite insulators are increasingly popular, providing weight savings and flexibility, which can be particularly advantageous in regions prone to severe weather conditions. Furthermore, the selection process should account for local pollution characteristics, as areas with higher pollution may require insulators with superior insulation properties to mitigate degradation over time.
Ultimately, understanding the intricacies of medium voltage insulators not only aids in maintaining the integrity of electrical systems but also contributes to improved operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. Historical data suggests that choosing the appropriate insulator can lead to a decrease in failures by up to 50%, which significantly enhances overall grid reliability and performance.
| Insulator Type | Material | Voltage Rating (kV) | Diameter (mm) | Weight (kg) | Environmental Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain Insulator | Porcelain | 36 | 200 | 3.5 | Polluted |
| Composite Insulator | Silicone Rubber | 24 | 180 | 2.2 | Coastal |
| Glass Insulator | Glass | 20 | 150 | 2.8 | Normal |
| Polymer Insulator | Polymeric Material | 15 | 160 | 2.0 | Ice |
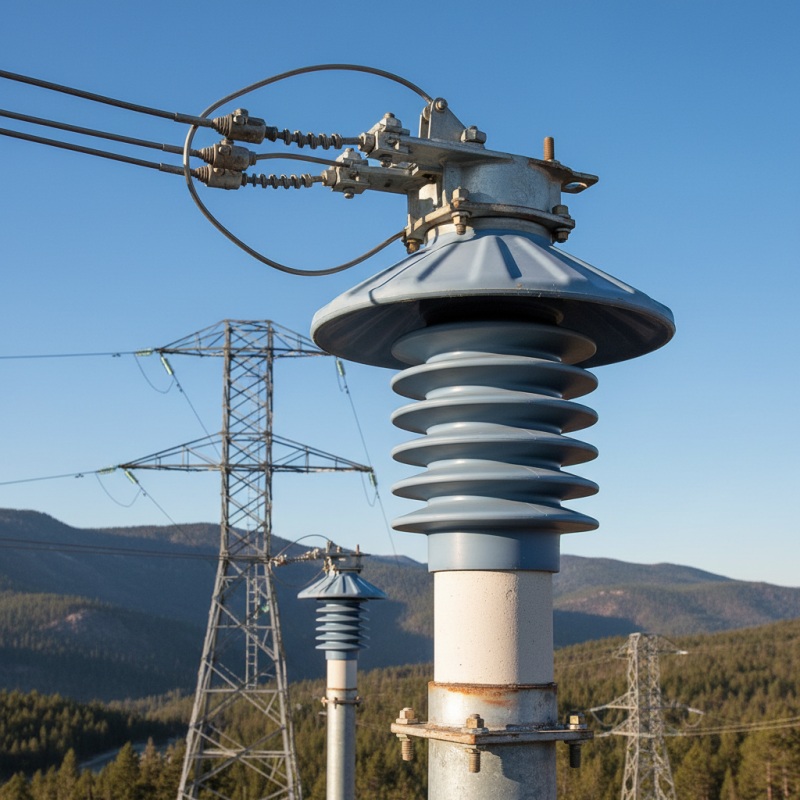

When selecting the right medium voltage insulator for your electrical system, understanding the various types available is crucial. Medium voltage insulators primarily encompass ceramic, glass, and polymer insulators, each with distinct properties that cater to specific applications. According to industry reports by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ceramic insulators have been the standard for decades, known for their durability and resistance to environmental factors. However, the weight and fragility of ceramics can sometimes be a drawback, especially in remote or rugged installations.
In contrast, glass insulators offer excellent electrical properties and visibility, making them easy to inspect for defects. A report by the IEEE indicates that glass insulators can survive extreme weather conditions, thereby enhancing longevity and reliability. Meanwhile, polymer insulators are gaining popularity due to their lightweight design and resistance to pollution, which is essential in coastal areas. Studies suggest that polymer insulators have up to 30% less leakage current compared to their ceramic counterparts, making them suitable for harsh environments. As the demand for efficient and durable electrical systems grows, understanding these comparative advantages allows engineers to make informed decisions about which type of insulator will best meet their operational needs.
When selecting medium voltage insulators for your electrical system, several critical factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and longevity. One of the primary considerations is the environmental conditions in which the insulators will operate. Different materials exhibit varying degrees of resistance to environmental stressors, such as UV radiation, pollution, and moisture.
An insulator's ability to withstand these factors directly influences its durability and effectiveness. Therefore, assessing the local climate and any potential exposure to contaminants is essential for making an informed decision.
Additionally, the electrical properties of the insulator material should be evaluated. Insulators need to support the voltage level of the system and maintain integrity under electrical stress. The dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength of the chosen materials play a significant role in their overall performance. Adequate sizing and spacing of the insulators are also crucial to minimize leakage currents and ensure safety. Finally, consider the installation and maintenance requirements of the insulators, as ease of handling can impact the overall efficiency of the electrical system. By carefully weighing these factors, you can select the most appropriate medium voltage insulators that align with your operational needs and environmental conditions.
Environmental conditions play a crucial role in determining the suitability of medium voltage insulators for electrical systems. Factors such as temperature, humidity, pollution levels, and the potential for environmental contaminants must be meticulously evaluated. For instance, insulators exposed to high levels of pollution, like industrial areas or coastal environments, require materials that can resist contamination and corrosion. Selecting insulators made of durable composites or ceramics can provide superior performance in such harsh conditions, ensuring long-lasting reliability.
Another critical aspect is the climate in which the electrical system operates. In regions subjected to extreme temperatures, whether very hot or very cold, insulators must be chosen for their thermal performance and their ability to maintain dielectric strength. Additionally, areas prone to heavy precipitation or freezing conditions necessitate insulators that can withstand these stresses without compromising their integrity. Understanding local weather patterns helps in selecting insulators that effectively minimize maintenance needs and enhance system resilience, thus ensuring safe and efficient operation in variable environments.
When it comes to medium voltage insulators, proper installation and maintenance are critical for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your electrical system. Begin the installation process by ensuring that you have the right tools and personal protective equipment. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines closely, as variations in materials or environmental conditions can affect how insulators should be set up. Make sure to inspect the installation area for any potential hazards, including uneven surfaces, moisture, or chemical exposure that could compromise the integrity of the insulator.
Tips for installation include using a torque wrench to ensure that all fittings are tightened to the recommended specifications. This helps avoid damage from over-tightening and ensures a secure fit. Additionally, implement a clear labeling system for components during installation to streamline future maintenance processes.
Maintenance is equally important in prolonging the lifespan of medium voltage insulators. Regular visual inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear, contamination, or physical damage. Cleaning the insulators with a non-corrosive solution can also prevent accumulation of dirt and pollutants that may lead to premature failure.
Remember, it's often beneficial to maintain a schedule for routine inspections and cleaning tasks. This proactive approach not only enhances safety but also significantly reduces the likelihood of costly repairs down the line.